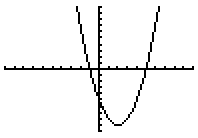
Factored Form
Quadratic Equations
When a quadratic function crosses the x-axis, those x-values are called the roots or zeros of the function. For a quadratic function that has real roots,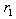 and
and 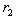 , the factored form is given as:
, the factored form is given as: 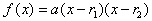 ; where a is a real number that works the same way as the a-value in the last lesson.
; where a is a real number that works the same way as the a-value in the last lesson.
For example: See how the graph of |
|
The factored form of a quadratic equation also tells you where the x-intercepts are located. The x-intercepts of the equation are the x-values that will make y = 0.